Follow Us:
WEB 3: A New Era of the Internet

Since Facebook changes its company name to Meta, WEB 3.0 is becoming the most popular term these days. So, in today’s article, we’ll jump into the sea of web3.0 and will try to understand it in a very easy way.
What is Web 3?
Web 3.0 is not implemented yet so we don’t have a strong definition. But we can define this term like this.
Web 3.0, also known as Semantic Web is the third generation of web service for websites as well as applications, with a goal of intellectual connection among users.
From the user end, we’ll divide the web service, like this-
- WEB 1.0: Only read
- WEB 2.0: Read and Write
- WEB 3.0: ??
Let’s find out from the beginning.
WEB 1.0:
Web 1.0 was the first edition of the web which lasted from 1989 to 2005. It was defined as a web of information. The innovator of the World Wide Web(www), Tim Berners-Lee considers the Web a “Read-Only Web”(ROW). It provides very little interaction where consumers can exchange the information together but it was not possible to interact with the website. The role of
the web was very passive. Web 1.0 was defined as ” It is an information space in which the items of
interest referred to as resources are identified by a global identifier called Uniform Resources Identifiers (URIs) “. The First-generation Web was an era of static pages and content delivery purposes only. In other words, the
early web allowed us to search for information and read it. There was very little in the way of user interaction or content contribution.
Basic Characteristics:
- Protocol: HTTP(Hypertext Transfer Protocol) & URL(Uniform Resource Locator).
- Content: Web 1.0 supported read-only contents only.
- Web 1.0 technology used static web pages made with simple HTML.
- Contents are provided from the server’s filesystem rather than a relational database management system (RDBMS).
Limitations:
Now let’s see the limitations of web 1.0.
- The main limitation of web 1.0 technology was the contents. The contents are understandable to only the humans but not to the machine.
- In web 1.0, no dynamic representation was there, no web console, and no such management like Google Webmaster was there (as the contents were not understandable for the machine). So, this is also a limitation of web 1.0.
- Also, as it is a one-directional web system, users can’t do much things in web 1.0.
WEB 2.0:

Web 2.0 is the second generation of the web. It was defined by Dale Dougherty in 2004 as a “Read-Write Web”(RWW). The technologies of web 2.0 allow assembling and managing large global crowds with common interests in social interactions. The timespan of Web 2.0 is 2004-2016.
“Web 2.0 is the business revolution in the computer industry caused by the move to the
Tim O’Reilly
internet as a platform, and any attempt to understand the rules for success on that new
platform. Chief among those rules is this: Build applications that harness network effects to get
better the more people to use them.”
This version of the web make some major properties like participatory, collaborative, and distributed practices. In other words, it is a bi-directional web system where users also can contribute to any topic or something like that. Basically, in Web 2.0, users can communicate with other users. This enables formal and informal spheres of daily activities ongoing on the web. In other terms, Web 2.0 includes “relationship” technologies, participatory media and social digital technology. And that’s why Web 2.0 is also called as “Social Web”. Consumer-centric web and the participant is taken into concern and which facilities reading and writing on the web makes the web transaction bi-directional. Web 2.0 is a web platform where users can leave many of the controls they have used in web 2.0. In other words, the user of web 2.0 has more interaction with less
control. Web 2.0 is not only a new version of web 1.0 but it also implies flexible web design, creative reuse, updates, collaborative content creation and modification in web 2.0 that should be considered as one of the outstanding features of web 2.0 is to support collaboration and to help gather collective intelligence rather Web 1.0.
Categories:
After introducing Web 2.0, it divides into some categories.
- Blogging
- Podcasting
- Social Networking
- Tagging
- RSS Feed
- Social Media
- Review site
All these are some examples of Web 2.0.
Basic Charactersitics:
- Web 2.0 offers the same freedom to contribute to almost all users. In other words, Web 2.0 is a bi-directional web. That’s why Web 2.0 is also known as Social web.
- Not like Web 1.0, Web 2.0 supports dynamic web pages.
- Web 2.0 technology also increase the user experience and looks after the user participation, Web standards, scalability, Metadata and many more things.
- Protocol: In Web 2.0, there came a major change. As now in this technology anyone can contribute to the web, so there came some problems in which security of a website also a thing of concern. To deal with that Netscape Communications created HTTPS in 1994 for its Netscape Navigator web browser. Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure(HTTPS) was used with the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol.
- Where Web 1.0 has no such things like user generated content, but Web 2.0 allows that too. There are websites & apps these days where users can also put their inputs. Like- Facebook, Linked In, Quora etc.
Limitation:
Every technology has some limitations, Web 2.0 is not an exception.
- Web 2.0 is not only updated version of web 1.0 but also it came up with really some new and great things. But as we all know that everything has their own pros and cons, it also that. In web 2.0 it gives user a power to contribute in the web. But at the same time it creates a centralized environment. Means the data of the users are being saved in some data servers.
- Privacy is also matter of concern. When the web become accessible for everyone, ethical issues becomes a concern of Web 2.0.
Now let’s talk about Web 3.0.
WEB 3.0:

WEB 3.0: SEMANTIC WEB
Web 3.0 is one of the modern and evolutionary topics associated with the following initiatives of Web 2.0. The term “Web 3.0”, was coined by Ethereum co-founder and Polkadot creator Gavin Wood in 2014. Web 3.0 can be also known as the “semantic Web”. The basic concept of web 3.0 revolves around creating a decentralized internet, which is completely polls apart of the concept of Web 2.0.
Blockchain is a perfect example of Web 3.0 technology.
Some technologists and intelligencers have described Web3 as a possible result to their enterprises about the over-centralization of the web in many”Big Tech” companies. Some have expressed that Web3 could ameliorate data security, scalability, and sequestration beyond what’s possible on traditional Web2.0 platforms.
Some legal academics expressed enterprises over the difficulty of regulating a decentralized web. They reported this which might make it more delicate to help cybercrimes, online importunity, detest speech, and dispersion of child abuse images. Some other critics of Web3 see the conception as a part of a cryptocurrency bubble or as an extension of blockchain-grounded trends that they view to be overhyped or dangerous, particularly NFTs. Some critics have raised enterprises about the environmental impact of cryptocurrencies and NFTs. Others have expressed beliefs that Web3 and the associated technologies are an aggregate scheme. Disharmony’s CEO, Jason Citron, twittered a screenshot in November 2021 suggesting the company might be exploring integrating Web3 into their platform. This led some to cancel their paid subscriptions over their nausea for NFTs, and others expressed to enterprises that such a change might increase the number of swindles and spam they had formerly endured on crypto-related Disharmony waiters. Two days latterly, Citron twittered that the company had no plans to integrate Web3 technologies into their platform, and said that it was an internal-only conception that had been developed in a company-wide hackathon.
Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is a growing list of records, denoted as blocks, that are linked together using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the former block, a timestamp, and trade data ( generally represented as a Merkle tree). The timestamp proves that the trade data was when the block was published to get into its hash. As blocks each contain information about the block former to it, they form a chain, with each fresh block buttressing the bones before it. Therefore, blockchains are resistant to modification of their data because formerly recorded, the data in any given block can’t be altered retroactively without altering all posterior blocks.
What is Semantic Web?
The Semantic Web ( occasionally known as Web3.0) is an extension of the World Wide Web through norms set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The thing of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, technologies similar to Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL) are used. These technologies are used to formally represent metadata. For illustration, ontology can describe generalities, connections between realities, and orders of effects. These bedded semantics offer significant advantages similar to logic over data and operating with miscellaneous data sources.
These norms promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, unnaturally the RDF. According to the W3C, “The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be participated and reused across the operation, enterprise, and community boundaries.”The Semantic Web is thus regarded as an integrator across different content and information operations and systems.
Characteristics:
Web 3.0 comes with some new concepts with some new characteristics.
- Semantic Web
- Connectivity (for which we can also compare it with Metaverse. Read this to know more- The Secrets Of Metaverse And Web 3.0)
- AI: In web 3.0, machines are able to distinguise information like an human to provide faster and more accurate/ relevant results. For Example, Google Search Console (GSC).
- Personalisation: Web personalisation is also upgrading in Web 3.0 where now more dynamic and
Challenges:
Instead of saying Limitation, we will call it challenges, as this is a new concept and still it is implemented.
- Vastness of Contents: Now in the present time, there are billions of pages with billions of contents exits in the (www) World Wide Web. So, managing this huge ammount of contents are really a challenging thing.
- Vagueness : With a huge number of user base it is quite difficult to understand what an user actually wants to search. So this is another challenge to resolve.
- Consistency: Inconsistent data can lead to logical contradiction and predictive analysis.
- Deceit: Although Artificial Intelligence (AI) can help in filtering data, what if all the data provided by th AI is intentionally wrong and misleading. Cryptography techniques are currently utilized to stop this problem. (We suggest you to read this article to understand it better- Is Artificial Intelligence a threat to humanity – Scientific World.)
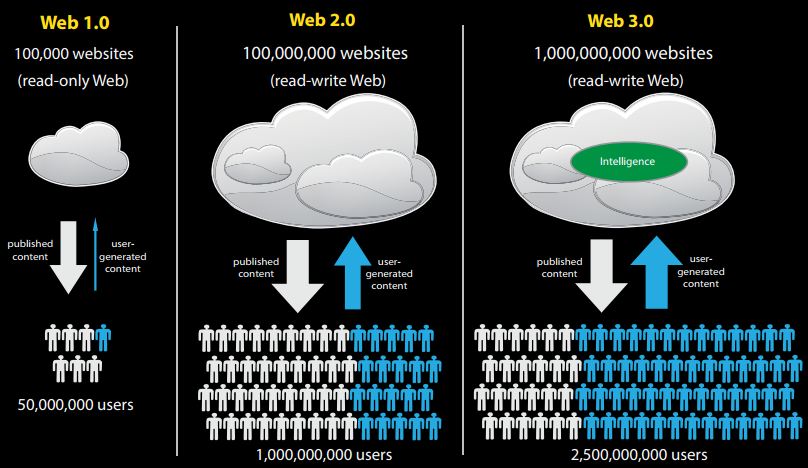
To represent the difference between WEB 1.0, WEB 2.0 & WEB 3.0, Research Hub created this great image presentation. You can clearly understand what is the main difference between these 3 web services.
Video Reference:
If you understand Hindi, then watch this video.
If you prefer to understand this topic in English then here is another video for you-



